Bacterial Serotyping Antisera

Bacterial typing and subtyping methods are necessary for the characterisation of disease-causing bacteria and are useful in providing epidemiological information.
This information is used for early outbreak identification, outbreak characterization and interventions to limit the impact of outbreaks on human populations.
Surveillance of the types and subtypes of bacteria circulating among humans, animals, food and the environment, provides information essential for the understanding on how the human population in the world is exposed to bacterial pathogens and how such exposures can be minimised or even eliminated. The determination of serotype prevalence has often paved the way for vaccines to prevent bacterial infections.
One of the most widely used techniques for the identification of bacterial types is based on the use of polyvalent and monovalent antisera, which react with one or more of the specific bacterial antigen groups.
Bacterial antigens are divided into 3 main groups:-
Cell wall (O antigen)
Flagella (H antigen)
Capsule (K antigen)
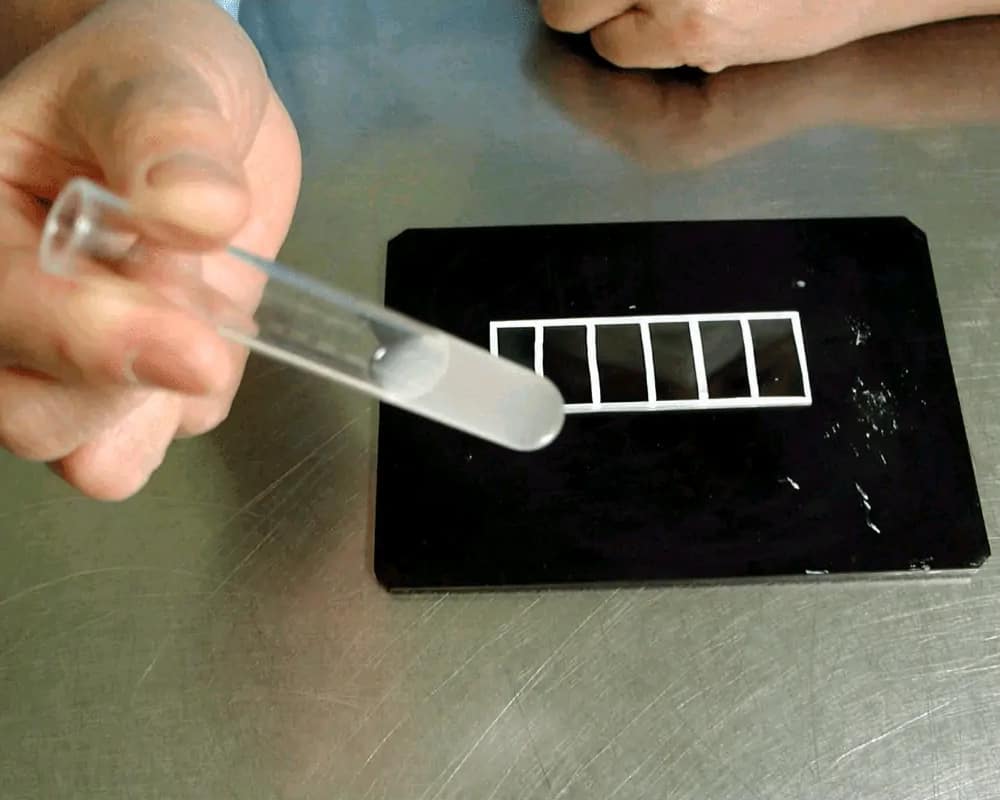
Slide Agglutination Test
Antisera for O and K typing are normally used with the slide agglutination test. Following isolation or enrichment of bacteria from a clinical specimen by using agar or broth, procurement of a pure culture from the primary culture and then identification of the bacterium by microscopy, growth characteristics and other biochemical properties, a small amount of dense antigen suspension (usually 5 – 10µL) is mixed with one of the selected antisera. After mixing, any agglutination patterns are macroscopically observed.
Test results can be obtained within one minute.


Tube Agglutination Test
Typing of H antigen is often performed by tube agglutination. Following the preparation of diluted H antigen suspension from a broth culture, 0.1mL of Antisera is added to 0.5mL of suspension in a tube, mixed and incubated at 50oC for one hour, and checked for agglutination.
Click on the red links below to open the full list of antisera available or click this link to download a pdf of all antisera.
Campylobacter Antisera
Campylobacter is a gram-negative spirally curved rod with bipolar flagella. Eleven species of Campylobacter have been identified, in which Campylobacter jejuni is reported as the most common species that cause enteric infection in humans.
There are two internationally accepted serotyping methods for Campylobacter, Penner’s serotyping using heat-stable antigens, and the other using heat-labile antigens. This product is for Campylobacter jejuni serogrouping based on Penner’s scheme by the passive hemagglutination (PHA) method.
To download a copy of the IFU (Instructions for Use), please click here.
| 270238 | Campylobacter As Gp A | 2mL |
| 270245 | Campylobacter As Gp B | 2mL |
| 270252 | Campylobacter As Gp C | 2mL |
| 270269 | Campylobacter As Gp D | 2mL |
| 270276 | Campylobacter As Gp E | 2mL |
| 270283 | Campylobacter As Gp F | 2mL |
| 270290 | Campylobacter As Gp G | 2mL |
| 270306 | Campylobacter As Gp I | 2mL |
| 270313 | Campylobacter As Gp J | 2mL |
| 270320 | Campylobacter As Gp K | 2mL |
| 270337 | Campylobacter As Gp L | 2mL |
| 270344 | Campylobacter As Gp N | 2mL |
| 270351 | Campylobacter As Gp O | 2mL |
| 270368 | Campylobacter As Gp P | 2mL |
| 270375 | Campylobacter As Gp R | 2mL |
| 270382 | Campylobacter As Gp S | 2mL |
| 270399 | Campylobacter As Gp U | 2mL |
| 270405 | Campylobacter As Gp V | 2mL |
| 270412 | Campylobacter As Gp Y | 2mL |
| 270429 | Campylobacter As Gp Z | 2mL |
| 270436 | Campylobacter As Gp Z2 | 2mL |
| 270443 | Campylobacter As Gp Z4 | 2mL |
| 270450 | Campylobacter As Gp Z5 | 2mL |
| 270467 | Campylobacter As Gp Z6 | 2mL |
| 270474 | Campylobacter As Gp Z7 | 2mL |
| 270481 | Campylobacter Reference As | 2mL |
Escherichia coli Antisera
Escherichia coli are a group of gram negative bacilli belonging to the family Enterobacteriaceae and considered as one of the bacteria in the human intestinal normal microbial flora. Their serological types are determined in combination with somatic antigens (O group: O1-O173) and flagella antigen (H type: H1-H56).
The E. coli that cause intestinal infectious diseases including diarrhoea, acute gastritis or colitis are referred to as pathogenic E. coli, which are classified into the following 4 groups according to differences in the mode of pathogenicity; enteropathogenic E. coli (EPEC), enteroinvasive E. coli (EIEC), enterotoxigenic E. coli (ETEC) and enterohemorrhagic E. coli (EHEC). Although the identification of pathogenic E. coli requires verification of their pathogenicity, pathogenic E. coli have often specific serotypes; therefore, typing of the serogroup and serotype is necessary for screening pathogenic E. coli.
These are liquid products of O- and H-sera containing specific agglutinins for serotyping of E. coli. O Group sera are prepared by hyperimmunizing healthy pigs (polyvalent sera) or healthy rabbits (monovalent sera) with reference strains of the organisms with each serotype inactivated by formalin, heated at 56°C for 30 minutes, removing cross agglutinins by absorption and antiseptically filtrated. For the preparation of H-sera, healthy rabbits are immunized with flagella of E. coli. Group O sera are used for O-serotyping tests by slide agglutination, and H sera are for H serotyping tests by tube agglutination.
To download a copy of the IFU (Instructions for Use), please click here.
| 295361 | E.coli As H-10 | 5mL |
| 295378 | E.coli As H-11 | 5mL |
| 295385 | E.coli As H-12 | 5mL |
| 295392 | E.coli As H-16 | 5mL |
| 295408 | E.coli As H-18 | 5mL |
| 295415 | E.coli As H-19 | 5mL |
| 295422 | E.coli As H-2 | 5mL |
| 295439 | E.coli As H-20 | 5mL |
| 295446 | E.coli As H-21 | 5mL |
| 295453 | E.coli As H-27 | 5mL |
| 295460 | E.coli As H-28 | 5mL |
| 295477 | E.coli As H-34 | 5mL |
| 295484 | E.coli As H-4 | 5mL |
| 295491 | E.coli As H-40 | 5mL |
| 295507 | E.coli As H-41 | 5mL |
| 295514 | E.coli AS H-42 | 5mL |
| 295521 | E.coli As H-45 | 5mL |
| 295538 | E.coli As H-5 | 5mL |
| 295545 | E.coli As H-51 | 5mL |
| 295552 | E.coli As H-6 | 5mL |
| 295569 | E.coli As H-7 | 5mL |
| 295576 | E.coli As H-9 | 5mL |
| 295583 | E.coli As O 1 | 2mL |
| 215772 | E.coli As O 103 | 2mL |
| 295590 | E.coli As O 111 | 2mL |
| 295606 | E.coli As O 112ac | 2mL |
| 295613 | E.coli As O 114 | 2mL |
| 295620 | E.coli As O 115 | 2mL |
| 295637 | E.coli As O 119 | 2mL |
| 215789 | E.coli As O 121 | 2mL |
| 295644 | E.coli As O 124 | 2mL |
| 295651 | E.coli As O 125 | 2mL |
| 295668 | E.coli As O 126 | 2mL |
| 295675 | E.coli As O 127a | 2mL |
| 295682 | E.coli As O 128 | 2mL |
| 295699 | E.coli As O 136 | 2mL |
| 295705 | E.coli As O 142 | 2mL |
| 295712 | E.coli As O 143 | 2mL |
| 295729 | E.coli As O 144 | 2mL |
| 215796 | E.coli As O 145 | 2mL |
| 295736 | E.coli As O 146 | 2mL |
| 295743 | E.coli As O 148 | 2mL |
| 295750 | E.coli As O 15 | 2mL |
| 295767 | E.coli As O 151 | 2mL |
| 295774 | E.coli As O 152 | 2mL |
| 295781 | E.coli As O 153 | 2mL |
| 295798 | E.coli As O 157 | 2mL |
| 295804 | E.coli As O 158 | 2mL |
| 295811 | E.coli As O 159 | 2mL |
| 215802 | E.coli As O 161 | 2mL |
| 295828 | E.coli As O 164 | 2mL |
| 215819 | E.coli As O 165 | 2mL |
| 295835 | E.coli As O 166 | 2mL |
| 295842 | E.coli As O 167 | 2mL |
| 295859 | E.coli As O 168 | 2mL |
| 295866 | E.coli As O 169 | 2mL |
| 295873 | E.coli As O 18 | 2mL |
| 295880 | E.coli As O 20 | 2mL |
| 295897 | E.coli As O 25 | 2mL |
| 295903 | E.coli As O 26 | 2mL |
| 295910 | E.coli As O 27 | 2mL |
| 295927 | E.coli As O 28ac | 2mL |
| 295934 | E.coli As O 29 | 2mL |
| 295941 | E.coli As O 44 | 2mL |
| 295958 | E.coli As O 55 | 2mL |
| 295965 | E.coli As O 6 | 2mL |
| 295972 | E.coli As O 63 | 2mL |
| 215758 | E.coli As O 74 | 2mL |
| 295989 | E.coli As O 78 | 2mL |
| 295996 | E.coli As O 8 | 2mL |
| 296009 | E.coli As O 86a | 2mL |
| 215765 | E.coli As O 91 | 2mL |
| 215741 | E.coli As poly 9 | 2mL |
| 292490 | E.coli As poly II (alternative) | 2mL |
| 292506 | E.coli As poly III (alternative) | 2mL |
| 292513 | E.coli As poly IV (alternative) | 2mL |
| 296016 | Escherichia coli As poly 1 | 2mL |
| 296023 | Escherichia coli As poly 2 | 2mL |
| 296030 | Escherichia coli As poly 3 | 2mL |
| 296047 | Escherichia coli As poly 4 | 2mL |
| 296054 | Escherichia coli As poly 5 | 2mL |
| 296061 | Escherichia coli As poly 6 | 2mL |
| 296078 | Escherichia coli As poly 7 | 2mL |
| 296085 | Escherichia coli As poly 8 | 2mL |
| 295347 | Escherichia coli As set 1 | 2mLX51 |
| 295354 | Escherichia coli As set 2 | 5mLX22 |
| 213891 | Toxigenic E.coli pili As 987P | 5mL |
| 213877 | Toxigenic E.coli pili As K88 | 5mL |
| 213884 | Toxigenic E.coli pili As K99 | 5mL |
| 200457 | Toxigenic E.coli pili As set | 5mLX3 |
Haemophilus influenzae Antisera
Haemophilus influenzae is a short, non-motile, capsulated bacillus which does not form endospores.
These are antisera used for the serotyping of Haemophilus influenzae capsules and are liquid products that contain type-specific agglutinins.
When these products are used, the capsular type can be identified by slide agglutination.
The antisera are prepared by hyper-immunizing rabbits with bacterial strains with each of the 6 type specific capsules a, b, c, d, e, and f. After bleeding, the serum is separated, heated at 56°C for 30 minutes, absorbed to remove the non-specific agglutinins and sterilized by filtration. As a preservative, sodium azide is added at 0.08 w/v%.
To download a copy of the IFU (Instructions for Use), please click here.
| 293695 | Haemophilus influenzae As a | 2mL |
| 293701 | Haemophilus influenzae As b | 2mL |
| 293718 | Haemophilus influenzae As c | 2mL |
| 293725 | Haemophilus influenzae As d | 2mL |
| 293732 | Haemophilus influenzae As e | 2mL |
| 293749 | Haemophilus influenzae As f | 2mL |
| 293688 | Haemophilus influenzae As set | 2mLX6 |
Listeria Antisera
Listeria monocytogenes is a Gram-positive short-form bacillus having flagella, which does not form endospores. Taxonomically, eight bacterial strains belong to Listeria. Among these bacterial strains, one bacterial strain L. monocytogenes is considered pathogenic in humans and animals. These antisera are intended for O-antigen and H-antigen typing of L. monocytogenes and each antiserum is a liquid product that contains agglutinins specific to each antigen type. These antisera are prepared by hyper-immunizing rabbits with heat-inactivated whole cells or flagella, heating at 56°C for 30 minutes, and removing cross agglutinins by absorption and filtrating them through a sterilized membrane. Each antiserum contains 0.08 w/v% sodium azide as a preservative.
To download a copy of the IFU (Instructions for Use), please click here.
| 294494 | Listeria As H-A | 5mL |
| 294500 | Listeria As H-AB | 5mL |
| 294517 | Listeria As H-C | 5mL |
| 294524 | Listeria As H-D | 5mL |
| 294531 | Listeria As O Ⅰ | 2mL |
| 294548 | Listeria As O Ⅰ/Ⅱ | 2mL |
| 294555 | Listeria As O Ⅳ | 2mL |
| 294562 | Listeria As O Ⅴ/Ⅵ | 2mL |
| 294579 | Listeria As O Ⅵ | 2mL |
| 294586 | Listeria As O Ⅶ | 2mL |
| 294593 | Listeria As O Ⅷ | 2mL |
| 294609 | Listeria As O Ⅸ | 2mL |
| 294616 | Listeria As set | 2X8 5X4 |
Pseudomonas aeruginosa Antisera
Pseudomonas aeruginosa (P. aeruginosa) is a gram-negative bacillus with monotrichate flagellum and motility. It is of significance due to its effects caused by opportunistic infection.
These products are liquid sera which contain specific antibodies against O-group antigens and are used for O-serogrouping of P. aeruginosa by slide agglutination. The antisera are prepared by immunising rabbits with antigens prepared from reference strains that have been heated at 100°C for 60 minutes. After bleeding, the serum is separated, inactivated at 56°C for 30 minutes, absorbed to remove non-specific agglutinins and filtered under sterile conditions.
To download a copy of the IFU (Instructions for Use), please click here.
| 213587 | Pseudomonas aeruginosa As Gp A | 2mL |
| 213594 | Pseudomonas aeruginosa As Gp B | 2mL |
| 213600 | Pseudomonas aeruginosa As Gp C | 2mL |
| 213617 | Pseudomonas aeruginosa As Gp D | 2mL |
| 213624 | Pseudomonas aeruginosa As Gp E | 2mL |
| 213631 | Pseudomonas aeruginosa As Gp F | 2mL |
| 213648 | Pseudomonas aeruginosa As Gp G | 2mL |
| 213655 | Pseudomonas aeruginosa As Gp H | 2mL |
| 213662 | Pseudomonas aeruginosa As Gp I | 2mL |
| 213679 | Pseudomonas aeruginosa As Gp J | 2mL |
| 213686 | Pseudomonas aeruginosa As Gp K | 2mL |
| 213693 | Pseudomonas aeruginosa As Gp L | 2mL |
| 213709 | Pseudomonas aeruginosa As Gp M | 2mL |
| 213716 | Pseudomonas aeruginosa As Gp N | 2mL |
| 213556 | Pseudomonas aeruginosa As poly Ⅰ | 2mL |
| 213563 | Pseudomonas aeruginosa As poly Ⅱ | 2mL |
| 213570 | Pseudomonas aeruginosa As poly Ⅲ | 2mL |
| 200372 | Pseudomonas aeruginosa Grouping As set | 2mLX17 |
Salmonella Antisera
Salmonella belongs to the family Enterobacteriaceae, is a gram negative, non-spore forming rod shaped bacillus, and the cause many types of infections from mild gastroenteritis to life threatening typhoid fever. Salmonella can be serotyped according to somatic antigens O (group O: O 2 – O 67), surface Vi, phase I flagellar and phase II flagellar (H types: H-a – H-z81) antigens. The somatic O antigens are heat stable and upon which grouping of the organism is based. The H antigens are heat labile and usually associated with motility. H antigen exists in two phases: phase I and phase II.
Deben Diagnostics Salmonella antisera are liquid products, containing specific agglutinins for each group O antigen, Vi antigen and H antigen, that are used for the serological identification of various Salmonella serotypes according to Kauffman-White classification. The antisera are prepared by hyper-immunizing healthy rabbits with reference strains, heating to 56°C for 30 minutes or using formalin treatment, removing analogous agglutinins by suction, before antiseptic filtration. For the preparation of H antisera, reference strains of the organisms killed by formalin treatment are used as an antigen, and for the preparation of Vi serum, Citrobacter ballerup, a strain that has Vi antigen, is used.
Group O antisera are used for the determination test of Salmonella serotypes using slide agglutination, and H antisera using tube agglutination or slide agglutination.
The antisera are available monovalent or polyvalent, singularly or in sets.
To download a copy of the IFU (Instructions for Use), please click here.
| 290793 | Salmonella As H-z29 | 2mL |
| 292421 | Salmonella As H Polyvalent phase 1 & 2 | 2mL |
| 292445 | Salmonella As H Rapid 1 | 2mL |
| 292452 | Salmonella As H Rapid 2 | 2mL |
| 292469 | Salmonella As H Rapid 3 | 2mL |
| 290571 | Salmonella As H-1 | 2mL |
| 294043 | Salmonella As H-1 | 5mL |
| 290625 | Salmonella As H-2 | 2mL |
| 294135 | Salmonella As H-2 | 5mL |
| 290632 | Salmonella As H-5 | 2mL |
| 294142 | Salmonella As H-5 | 5mL |
| 290649 | Salmonella As H-6 | 2mL |
| 294159 | Salmonella As H-6 | 5mL |
| 290656 | Salmonella As H-7 | 2mL |
| 294166 | Salmonella As H-7 | 5mL |
| 290458 | Salmonella As H-a | 2mL |
| 293923 | Salmonella As H-a | 5mL |
| 290465 | Salmonella As H-b | 2mL |
| 293930 | Salmonella As H-b | 5mL |
| 290472 | Salmonella As H-c | 2mL |
| 293947 | Salmonella As H-c | 5mL |
| 290489 | Salmonella As H-d | 2mL |
| 293954 | Salmonella As H-d | 5mL |
| 292520 | Salmonella As H-E (Complex) | 2mL |
| 290496 | Salmonella As H-e,h | 2mL |
| 293961 | Salmonella As H-e,h | 5mL |
| 290564 | Salmonella As H-e,n | 2mL |
| 294036 | Salmonella As H-e,n | 5mL |
| 290670 | Salmonella As H-f | 2mL |
| 294180 | Salmonella As H-f | 5mL |
| 290502 | Salmonella As H-G | 2mL |
| 293978 | Salmonella As H-G | 5mL |
| 291882 | Salmonella As H-g,p | 5mL |
| 290519 | Salmonella As H-i | 2mL |
| 293985 | Salmonella As H-i | 5mL |
| 290526 | Salmonella As H-k | 2mL |
| 293992 | Salmonella As H-k | 5mL |
| 294005 | Salmonella As H-L | 5mL |
| 290687 | Salmonella As H-m | 2mL |
| 294197 | Salmonella As H-m | 5mL |
| 290694 | Salmonella As H-p | 2mL |
| 294203 | Salmonella As H-p | 5mL |
| 290700 | Salmonella As H-q | 2mL |
| 294210 | Salmonella As H-q | 5mL |
| 290540 | Salmonella As H-r | 2mL |
| 294012 | Salmonella As H-r | 5mL |
| 290717 | Salmonella As H-s | 2mL |
| 294227 | Salmonella As H-s | 5mL |
| 290724 | Salmonella As H-t | 2mL |
| 294234 | Salmonella As H-t | 5mL |
| 290823 | Salmonella As H-u | 2mL |
| 294241 | Salmonella As H-u | 5mL |
| 290588 | Salmonella As H-v | 2mL |
| 294098 | Salmonella As H-v | 5mL |
| 290595 | Salmonella As H-w | 2mL |
| 294104 | Salmonella As H-w | 5mL |
| 290762 | Salmonella As H-x | 2mL |
| 294289 | Salmonella As H-x | 5mL |
| 290557 | Salmonella As H-y | 2mL |
| 294029 | Salmonella As H-y | 5mL |
| 290809 | Salmonella As H-z | 2mL |
| 294050 | Salmonella As H-z | 5mL |
| 290786 | Salmonella As H-z10 | 2mL |
| 294074 | Salmonella As H-z10 | 5mL |
| 290601 | Salmonella As H-z13 | 2mL |
| 294111 | Salmonella As H-z13 | 5mL |
| 290779 | Salmonella As H-z15 | 2mL |
| 294296 | Salmonella As H-z15 | 5mL |
| 290731 | Salmonella As H-z23 | 2mL |
| 294258 | Salmonella As H-z23 | 5mL |
| 290748 | Salmonella As H-z24 | 2mL |
| 294265 | Salmonella As H-z24 | 5mL |
| 290618 | Salmonella As H-z28 | 2mL |
| 294128 | Salmonella As H-z28 | 5mL |
| 294081 | Salmonella As H-z29 | 5mL |
| 290755 | Salmonella As H-z32 | 2mL |
| 294272 | Salmonella As H-z32 | 5mL |
| 290816 | Salmonella As H-z4 | 2mL |
| 294067 | Salmonella As H-z4 | 5mL |
| 290663 | Salmonella As H-z6 | 2mL |
| 294173 | Salmonella As H-z6 | 5mL |
| 294302 | Salmonella As O 1,3,19 | 2mL |
| 294319 | Salmonella As O 11 | 2mL |
| 294326 | Salmonella As O 13 | 2mL |
| 294333 | Salmonella As O 16 | 2mL |
| 292575 | Salmonella As O 17 | 2mL |
| 294340 | Salmonella As O 18 | 2mL |
| 294364 | Salmonella As O 2 | 2mL |
| 294371 | Salmonella As O 21 | 2mL |
| 292582 | Salmonella As O 28 | 2mL |
| 294388 | Salmonella As O 3,10 | 2mL |
| 294395 | Salmonella As O 35 | 2mL |
| 292599 | Salmonella As O 39 | 2mL |
| 294401 | Salmonella As O 4 | 2mL |
| 291875 | Salmonella As O 6 | 2mL |
| 294418 | Salmonella As O 6,14 | 2mL |
| 294425 | Salmonella As O 7 | 2mL |
| 294432 | Salmonella As O 8 | 2mL |
| 294449 | Salmonella As O 9 | 2mL |
| 294456 | Salmonella As O 9,46 | 2mL |
| 292537 | Salmonella As Omnivalent | 2mL |
| 211910 | Salmonella As phase H-1 | 5mL |
| 211798 | Salmonella As phase H-a | 5mL |
| 211804 | Salmonella As phase H-b | 5mL |
| 211811 | Salmonella As phase H-c | 5mL |
| 211828 | Salmonella As phase H-d | 5mL |
| 211835 | Salmonella As phase H-e,h | 5mL |
| 211903 | Salmonella As phase H-e,n | 5mL |
| 211842 | Salmonella As phase H-G | 5mL |
| 211859 | Salmonella As phase H-i | 5mL |
| 211866 | Salmonella As phase H-k | 5mL |
| 211873 | Salmonella As phase H-L | 5mL |
| 211880 | Salmonella As phase H-r | 5mL |
| 211897 | Salmonella As phase H-y | 5mL |
| 211927 | Salmonella As phase H-z | 5mL |
| 211941 | Salmonella As phase H-z10 | 5mL |
| 211958 | Salmonella As phase H-z29 | 5mL |
| 211934 | Salmonella As phase H-z4 | 5mL |
| 200181 | Salmonella As phase Set | 17 x 5mL |
| 294463 | Salmonella As Polyvalent O | 2mL |
| 292483 | Salmonella As Polyvalent O (A-G) | 2mL |
| 292476 | Salmonella As Polyvalent O (A-S) | 2mL |
| 294357 | Salmonella As Polyvalent O 1 | 2mL |
| 293855 | Salmonella As Set 1 | 18 x 2mL |
| 293862 | Salmonella As Set 2 | 17 x 5mL |
| 293879 | Salmonella As Set 3 | 4 x 5mL |
| 293886 | Salmonella As Set 4 | 5 x 5mL |
| 293893 | Salmonella As Set 5 | 7 x 5mL |
| 293909 | Salmonella As Set 6 | 5 x 5mL |
| 293916 | Salmonella As Set 7 | 3 x 2mL, 2 x 5mL |
| 294470 | Salmonella As Vi | 2mL |
| 290533 | Salmonella H-L | 2mL |
Shigella Antisera
Shigella is a nonmotile gram-negative bacillus, belonging to the Enterobacteriaceae family. The organisms orally taken in invade the epithelial cells of the large intestine to cause shigellosis with (mucous and bloody) diarrhoea, fever and abdominal pain as chief complaints. Shigella is classified into the following 4 species by serological properties of somatic antigens (O antigens) and biochemical properties according to the recommendation (1984) of the International Enterobacteriaceae Grouping Subcommittee based on Ewing’s proposal in 1949: S. dysenteriae (subgroup A), S. flexneri (subgroup B), S. boydii (subgroup C) and S. sonnei (subgroup D). S. dysenteriae is classified into 12 serologic types by antigen type, S. flexneri into 6 serotypes and 13 subtypes by antigen type and group, S boydii into 18 serotypes by antigen type. There is one serotype as for S. sonnei, which is classified into 2 antigens, phase I (smooth: S type) and phase II (rough: R type) according to the S-R mutation of the O antigen.
These products are polyvalent sera or monovalent sera used for serotyping of Shigella by slide agglutination, each of which contains a specific agglutinin. Each polyvalent serum is prepared by hyperimmunizing healthy pigs with the inactivated organisms, heating the obtained serum at 56°C for 30 minutes, removing analogous agglutinins with suction and aseptically filtrating them. As for monovalent sera, healthy rabbits are hyperimmunized to obtain sera.
To download a copy of the IFU (Instructions for Use), please click here.
| 295095 | Shigella As boydii 1 | 2mL |
| 295101 | Shigella As boydii 10 | 2mL |
| 295118 | Shigella As boydii 11 | 2mL |
| 295125 | Shigella As boydii 12 | 2mL |
| 295132 | Shigella As boydii 13 | 2mL |
| 295149 | Shigella As boydii 14 | 2mL |
| 295156 | Shigella As boydii 15 | 2mL |
| 295163 | Shigella As boydii 16 | 2mL |
| 295170 | Shigella As boydii 17 | 2mL |
| 295187 | Shigella As boydii 18 | 2mL |
| 295200 | Shigella As boydii 2 | 2mL |
| 295224 | Shigella As boydii 3 | 2mL |
| 295248 | Shigella As boydii 4 | 2mL |
| 295255 | Shigella As boydii 5 | 2mL |
| 295262 | Shigella As boydii 6 | 2mL |
| 295279 | Shigella As boydii 7 | 2mL |
| 295286 | Shigella As boydii 8 | 2mL |
| 295293 | Shigella As boydii 9 | 2mL |
| 295309 | Shigella As boydii poly C | 2mL |
| 295194 | Shigella As boydii poly C1 | 2mL |
| 295217 | Shigella As boydii poly C2 | 2mL |
| 295231 | Shigella As boydii poly C3 | 2mL |
| 294852 | Shigella As dysenteriae 1 | 2mL |
| 294869 | Shigella As dysenteriae 10 | 2mL |
| 294876 | Shigella As dysenteriae 11 | 2mL |
| 294883 | Shigella As dysenteriae 12 | 2mL |
| 294906 | Shigella As dysenteriae 2 | 2mL |
| 294913 | Shigella As dysenteriae 3 | 2mL |
| 294920 | Shigella As dysenteriae 4 | 2mL |
| 294937 | Shigella As dysenteriae 5 | 2mL |
| 294944 | Shigella As dysenteriae 6 | 2mL |
| 294951 | Shigella As dysenteriae 7 | 2mL |
| 294968 | Shigella As dysenteriae 8 | 2mL |
| 294975 | Shigella As dysenteriae 9 | 2mL |
| 294982 | Shigella As dysenteriae poly A | 2mL |
| 294890 | Shigella As dysenteriae poly A1 | 2mL |
| 294999 | Shigella As flexneri (3)4 | 2mL |
| 295057 | Shigella As flexneri 6 | 2mL |
| 295071 | Shigella As flexneri 7(8) | 2mL |
| 295002 | Shigella As flexneri Ⅰ | 2mL |
| 295019 | Shigella As flexneri Ⅱ | 2mL |
| 295026 | Shigella As flexneri Ⅲ | 2mL |
| 295033 | Shigella As flexneri Ⅳ | 2mL |
| 295040 | Shigella As flexneri Ⅴ | 2mL |
| 295064 | Shigella As flexneri Ⅵ | 2mL |
| 295088 | Shigella As flexneri poly B | 2mL |
| 294821 | Shigella As set 1 | 2mLX49 |
| 294838 | Shigella As set 2 | 2mLX19 |
| 294845 | Shigella As set 3 | 2mLX8 |
| 295316 | Shigella As sonnei phaseⅠ | 2mL |
| 295323 | Shigella As sonnei phaseⅡ | 2mL |
| 295330 | Shigella As sonnei poly D | 2mL |
Staphylococcal Coagulase Antisera
Staphylococcus aureus (S. aureus) is a typical causal microorganism for purulent diseases such as wound infection and is a leading cause of food poisoning. It is also widely known as a cause of Staphylococcal Scalded Skin Syndrome (SSSS) and Toxic Shock Syndrome (TSS). Methicillin resistant Staphylococcus aureus (MRSA) is a known cause of nosocomial infections including serious sepsis and enteritis in patients with impaired immunological function or postoperative patients.
Free coagulase is produced extracellularly by S. aureus which coagulates human plasma or that of animals such as rabbits but is neutralised by antisera. This product is for typing of Staphylococcal coagulase and is prepared by hyperimmunising healthy rabbits with purified coagulase.
To download a copy of the IFU (Instructions for Use), please click here.
| 270061 | Staphylococcal Coagulase As Ⅰ | 5mL |
| 270078 | Staphylococcal Coagulase As Ⅱ | 5mL |
| 270085 | Staphylococcal Coagulase As Ⅲ | 5mL |
| 270092 | Staphylococcal Coagulase As Ⅳ | 5mL |
| 270108 | Staphylococcal Coagulase As Ⅴ | 5mL |
| 270115 | Staphylococcal Coagulase As Ⅵ | 5mL |
| 270122 | Staphylococcal Coagulase As Ⅶ | 5mL |
| 270139 | Staphylococcal Coagulase As Ⅷ | 5mL |
| 270016 | Staphylococcal Coagulase As set | 5mLX8 |
Streptococcus pneumoniae Antisera
Streptococcus pneumoniae (S. pneumoniae) is the most common cause of community-acquired bacterial pneumonia (CAP) and otitis media, and the second most common cause of meningitis in infants and children which may lead to learning disabilities and hearing impairment. Mortality occurs in approximately 10-15% of hospitalised adults with invasive disease. While vaccines are available, widespread overuse of antibiotics has contributed to the emergence of drug resistant strains.
S. pneumoniae is serotyped based on the antigenicity of the capsular polysaccharide. This product contains antibodies specific to the capsular antigens of S. pneumoniae. The sera are prepared by hyperimmunising healthy rabbits with reference strains (ATCC) of S. pneumoniae, heating at 56°C for 30 minutes, and removing cross agglutinins by absorption and aseptic filtration.
To download a copy of the IFU (Instructions for Use), please click here.
| 270054 | Streptococcus pneumoniae As set | 2mLX47 |
| 270542 | Streptococcus pneumoniae Poly 1 As | 2mL |
| 270559 | Streptococcus pneumoniae Poly 2 As | 2mL |
| 270566 | Streptococcus pneumoniae Poly 3 As | 2mL |
| 270573 | Streptococcus pneumoniae Poly 4 As | 2mL |
| 270580 | Streptococcus pneumoniae Poly 5 As | 2mL |
| 270597 | Streptococcus pneumoniae Poly 6 As | 2mL |
| 270603 | Streptococcus pneumoniae Poly 7 As | 2mL |
| 270610 | Streptococcus pneumoniae Poly 8 As | 2mL |
| 270627 | Streptococcus pneumoniae type 1 As | 2mL |
| 270719 | Streptococcus pneumoniae type 10 As | 2mL |
| 270726 | Streptococcus pneumoniae type 11 As | 2mL |
| 270733 | Streptococcus pneumoniae type 12 As | 2mL |
| 270740 | Streptococcus pneumoniae type 14 As | 2mL |
| 270757 | Streptococcus pneumoniae type 15 As | 2mL |
| 270764 | Streptococcus pneumoniae type 16 As | 2mL |
| 270771 | Streptococcus pneumoniae type 17 As | 2mL |
| 270788 | Streptococcus pneumoniae type 18 As | 2mL |
| 270795 | Streptococcus pneumoniae type 19 As | 2mL |
| 270634 | Streptococcus pneumoniae type 2 As | 2mL |
| 270801 | Streptococcus pneumoniae type 20 As | 2mL |
| 270818 | Streptococcus pneumoniae type 21 As | 2mL |
| 270825 | Streptococcus pneumoniae type 22 As | 2mL |
| 270832 | Streptococcus pneumoniae type 23 As | 2mL |
| 270849 | Streptococcus pneumoniae type 24 As | 2mL |
| 270856 | Streptococcus pneumoniae type 25 As | 2mL |
| 270863 | Streptococcus pneumoniae type 27 As | 2mL |
| 270870 | Streptococcus pneumoniae type 28 As | 2mL |
| 270887 | Streptococcus pneumoniae type 29 As | 2mL |
| 270641 | Streptococcus pneumoniae type 3 As | 2mL |
| 270894 | Streptococcus pneumoniae type 31 As | 2mL |
| 270900 | Streptococcus pneumoniae type 32 As | 2mL |
| 270917 | Streptococcus pneumoniae type 33 As | 2mL |
| 270924 | Streptococcus pneumoniae type 34 As | 2mL |
| 270931 | Streptococcus pneumoniae type 35 As | 2mL |
| 270948 | Streptococcus pneumoniae type 36 As | 2mL |
| 270955 | Streptococcus pneumoniae type 38 As | 2mL |
| 270962 | Streptococcus pneumoniae type 39 As | 2mL |
| 270658 | Streptococcus pneumoniae type 4 As | 2mL |
| 270979 | Streptococcus pneumoniae type 40 As | 2mL |
| 270986 | Streptococcus pneumoniae type 41 As | 2mL |
| 270993 | Streptococcus pneumoniae type 46 As | 2mL |
| 271006 | Streptococcus pneumoniae type 47 As | 2mL |
| 270665 | Streptococcus pneumoniae type 5 As | 2mL |
| 270672 | Streptococcus pneumoniae type 6 As | 2mL |
| 270689 | Streptococcus pneumoniae type 7 As | 2mL |
| 270696 | Streptococcus pneumoniae type 8 As | 2mL |
| 270702 | Streptococcus pneumoniae type 9 As | 2mL |
Vibrio cholerae Antisera
Vibrio cholerae (V. cholerae) belongs to the family Vibrionaceae, is a highly motile, gram-negative curved rod bacillus, and a cause of intestinal infection. Serological typing of V. cholerae is based on its O somatic antigens and is classified into over 200 types, although of these, only serotypes O1 and O139 are the causative agents of cholera, a highly contagious disease characterised by severe diarrhoea due to the production of toxins produced by the bacteria.
V. cholerae O1 strains are classified into biovar classical type and biovar eltor type according to their biological characteristics, and both consist of at least three types of antigenic factor: A, B, and C, leading strains to be classified into serovar Ogawa or Inaba according to the presence of factor B/C. The transitional type from serovar Ogawa to serovar Inaba is referred to as serovar Hikojima.
Deben Diagnostics V. cholerae antisera are liquid products that contain a specific agglutinin and are used for the serotyping of V. cholerae O1 and O139. The antisera are prepared by hyper-immunizing healthy rabbits with the reference strains. Antisera are separated, heated at 56°C for 30 minutes, non-specific agglutinins are removed, and then sterilized by filtration.
The antisera are available monovalent or O1 polyvalent, singularly or as an O1 set.
To download a copy of the IFU (Instructions for Use), please click here.
| 294487 | V. cholerae As O139 ‘Bengal’ | 2mL |
| 293824 | V. cholerae As Inaba | 2mL |
| 293848 | V. cholerae As Ogawa | 2mL |
| 293831 | V. cholerae Polyvalent As | 2mL |
| 293817 | V. cholerae As Set | 3 x 2mL |
Yersinia Antisera
Yersinia enterocolitica (Y. enterocolitica) is a Gram-negative short-form bacillus belonging to family Enterobacteriaceae. The Y. enterocolitica antisera are immune sera to be used for identifying groups O3, O5, O8 and O9 of Wauters’ classification of Y. enterocolitica by slide agglutination. These groups are considered as having conspicuous pathogenicity in humans. The antisera are liquid products that contain agglutinins specific to each group shown on the vial label. Each antiserum is prepared by hyperimmunising healthy rabbits with Wauters’ reference strains and inactivating the serum at 56°C for 30 minutes. After removing the cross agglutinins by absorption, the serum is sterilised by filtration.
To download a copy of the IFU (Instructions for Use), please click here.
| 293770 | Yersinia enterocolitica As O 3 | 2mL |
| 293787 | Yersinia enterocolitica As O 5 | 2mL |
| 293794 | Yersinia enterocolitica As O 8 | 2mL |
| 293800 | Yersinia enterocolitica As O 9 | 2mL |
| 293763 | Yersinia enterocolitica As poly O 1,2 | 2mL |
| 293756 | Yersinia enterocolitica O-As set | 2mLX5 |
| 215093 | Yersinia pseudotuberculosis As 1 | 2mL |
| 215109 | Yersinia pseudotuberculosis As 2 | 2mL |
| 215116 | Yersinia pseudotuberculosis As 3 | 2mL |
| 215123 | Yersinia pseudotuberculosis As 4 | 2mL |
| 215130 | Yersinia pseudotuberculosis As 5 | 2mL |
| 215147 | Yersinia pseudotuberculosis As 6 | 2mL |
| 200556 | Yersinia pseudotuberculosis As set | 2mLX6 |
Other Products Available
We have an extensive product range consisting of the following:
Please contact sales@debendiagnostics.co.uk for further details.